Part-2
Disease + Disease Interaction Modifiers
and details on HCC groupings 8 to 14
Read in the Part 1 edition of the 4-part series, we discussed the changes in demographic rates and the first 7 groupings of the V28 hierarchies. In this Part 2 edition of the 4-part series, we will examine the changes in the disease + disease interaction modifiers and cover the next 7 groupings.
Disease + Disease Interactions Modifiers
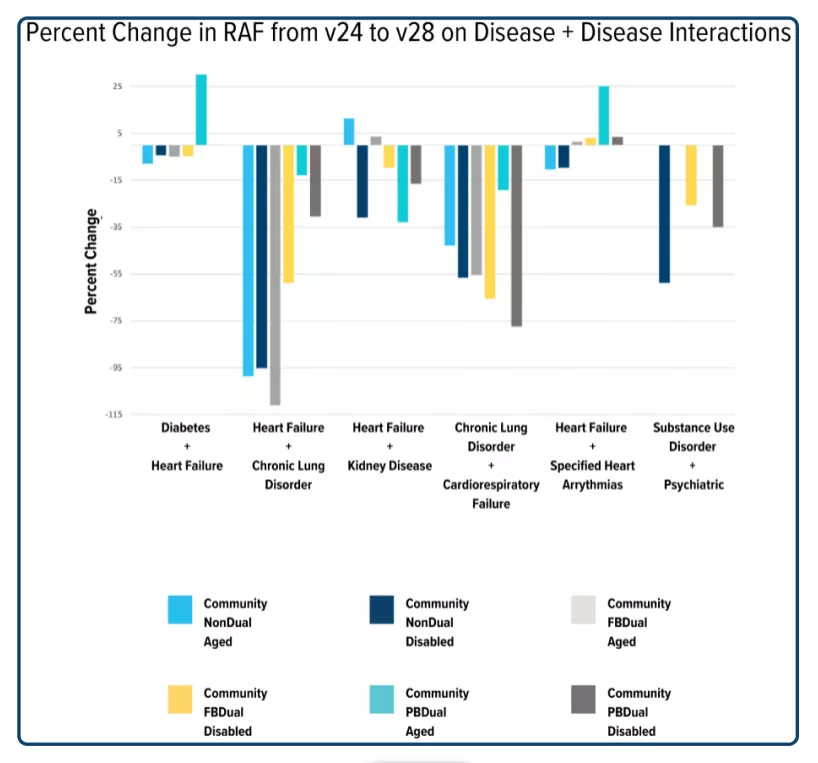
Taking care of a patient with multiple conditions is more expensive and difficult than taking care of patients with fewer conditions. Medicare recognizes this and includes an additional RAF value addition for patients that have certain combinations of HCCs. For example: if a patient is coded with diabetes and CHF, an additional modifier is added to the RAF score. Although HCCs were rearranged into new categories, all of the interaction categories from V24 are still present in V28, with one exception: immune disorders + cancer. The interaction of immune disorders and cancer has been eliminated, which traditionally added an additional RAF of 0.6-0.8 to each patient. Looking at the values of the interaction categories, the value of most groups decreased by 12% – 70%. Notably, two particular groupings had substantial increases and deviated from the other trends. These are the interaction of CHF and diabetes and the interaction between CHF and arrhythmias in the ‘partially dual-eligible aged’ population, with an increase of 31% and 25%, respectively.
HCC number changes and groupings part 2 of 4
In the Part-1 of the 4 Part Series, we covered the HCCs in the groupings for Infections Diseases, Neoplasms, Diabetes, Metabolic Diseases, Liver Diseases, Gastrointestinal Diseases, and Musculoskeletal diseases. In this part-2 of the series, we will cover the next 7 groupings, Blood Diseases to Arrest Diseases.
8) Blood Disease Group
This is one of the most drastically altered groupings. For the most part, HCC 47 (Disorders of Immunity) has been removed as an HCC. The other two HCCs in the V24 version of this grouping have had their ICD-10s have been spread across several different new categories. Overall this grouping has 7 different HCCs in it: 2 HCCs that address sickle cell disease, 3 HCCs addressing bleeding issues such as anemia, hemophilia, and immune thrombocytopenia, and lastly 2 HCCs for severe immunological disorders. The details of these changes are as follows
V24 HCC 46 (Severe Hematological Disorders) changes:
- –The codes for refractory anemia and refractory cytopenia have been moved to V28 HCC 19 (Myelodysplastic Syndromes, Multiple Myeloma, and Other Cancers) in the neoplasm grouping
- –The codes for sickle cell disease and thalassemias have been split between V28 HCC 107 (Sickle Cell Anemia (Hb-SS) and Thalassemia Beta Zero) and V28 108 (Sickle Cell Disorders, Except Sickle Cell Anemia (Hb-SS) and Thalassemia Beta Zero; Beta Thalassemia Major)
- Codes for sickle cell anemia and beta-thalassemia are placed in HCC 107 with an average RAF decrease of 1.584
- All other sickle cell disorders and Thalassemia codes have been moved to HCC 108 with an average RAF decrease of 2.345
- –The codes for hemolytic anemia and hemolytic uremic syndromes have been moved to HCC V28 109 (Acquired Hemolytic, Aplastic, and Sideroblastic Anemias) with an average RAF decrease of 1.294
- –The codes for drug-induced hemolytic and aplastic anemias have been removed from the model
V24 HCC 47 (Disorders of Immunity) changes
- –A large number of codes have been removed from the model, including some of the more commonly coded conditions such as neutropenia, secondary immunodeficiency, and drug-induced pancytopenia
- –Some of the more severe genetic immunological disorders such as SCID or common variable immunodeficiency have been moved to V28 HCC 114 (Common Variable and Combined Immunodeficiencies) with an average RAF increase of 1.756
- –Other less severe immunodeficiencies such as cyclic neutropenia or selective immunoglobulin deficiencies have been moved to V28 HCC 115 (Specified Immunodeficiencies and White Blood Cell Disorders) with an average RAF decrease of 0.138
- –The codes for graft-versus-host disease have been moved to V28 HCC 454 (Stem Cell, Including Bone Marrow, Transplant Status/Complications) with a RAF increase of 0.212
HCC 48 (Coagulation Defects and Other Specified Hematological Disorders) changes:
- –Many codes were removed from the model, most notably secondary hypercoagulable state, sickle cell trait, unspecified and drug-induced thrombocytopenia, and senile purpura
- –The codes for severe bleeding disorders such as Von Willebrand’s, primary thrombocytopenia, and other hereditary hemophilias have been moved to V28 HCC 112 (Immune Thrombocytopenia and Specified Coagulation Defects and Hemorrhagic Conditions) with an average RAF increase of 0.321
9) Cognitive Disease Group
This group has changed from classifying dementia as complicated or uncomplicated to placing codes into separate HCCs based on severity. Further details below:
V24 HCC 51 (Dementia With Complications) has been split between V28 HCC 125 (Dementia, Severe), 126 (Dementia, Moderate), or 127 (Dementia, Mild or Unspecified) based on if the ICD-10 code references severe, moderate, or mild dementia
- –Of note, all three severities and HCCs have the same RAF value. On average this leads to an RAF increase of 0.039
HCC 52 (Dementia Without Complication) has removed a few rare causes of dementia or dementia-like disorders such as Tay-Sachs, Krabbe disease, senile degen of brain unspecified, and degen of the nervous system due to EtOH.
- –The other codes have mostly been split between 125, 126, and 127 based on severity
- –Important codes to note are that Alzheimer’s disease, hydrocephalus, and Lewy body dementia all now fall into V28 HCC 127 (mild dementia)
DoctusTech is helping Value-Based Care organizations evaluate their RAF score in the new v28 model. Do you want to know what your organization's RAF score will look like in the new v28 model? Contact us for a detailed impact assessment analytic report.
10) Substance Use Disorder Disease Group
The conditions in this group have been reclassified into 5 groups based on disease severity, presence of psychotic symptoms, and the substance used. In detail:
V24 HCC 54 (Substance Use with Psychotic Complications) has been split into V28 HCC 135 (Drug Use with Psychotic Complications) or V28 136 (Alcohol Use with Psychotic Complications) based on if the disorder is due to EtOH or another substance.
- –Codes moving to HCC 135, drug use with psychotic disorder, have an average RAF increase of 0.172,
- –Codes moving to HCC 136, alcohol use with psychotic disorder, have an average RAF increase of 0.139
V24 HCC 55 (Substance Use Disorder, Moderate/Severe, or Substance Use with Complications) also has had its code split based on if the codes reference EtOH or other substances
- –EtOH or THC use or abuse with intoxication codes have been removed from the model
- –EtOH dependence, remission, withdrawal, and abuse or use with complications have all been moved to V28 HCC 139 (Alcohol Use Disorder, Moderate/Severe, or Alcohol Use with Specified Non-Psychotic Complications) with an average RAF decrease of 0.084
- –All other codes previously in V24 HCC 55 have been moved to V28 HCC 137 (Drug Use Disorder, Moderate/Severe, or Drug Use with Non-Psychotic Complications) with a RAF increase of 0.059
V24 HCC 56 (Substance Use Disorder, Mild, Except Alcohol and Cannabis) has had all of its codes moved to HCC 138 (Drug Use Disorder, Mild, Uncomplicated, Except Cannabis) with an RAF increase of 0.028
11) Psychiatric Disease Group
The conditions in this group have had some minor rearrangements. Depression and bipolar each now have their own HCCs, eating disorders have been added to the HCC for personality disorders, and all forms of nonschizophrenic psychosis now have their own HCC. In detail:
V24 HCC 57 (Schizophrenia) has had all its codes moved to V28 HCC 151 (Schizophrenia) with an RAF increase of 0.012
V24 HCC 58 (Reactive and Unspecified Psychosis) has had all its codes moved to all HCC 152 (Psychosis, Except Schizophrenia) with an RAF increase of 0.020
V24 HCC 59 (Major Depressive, Bipolar, and Paranoid Disorders) has been mostly split between HCC 154 (Bipolar Disorders without Psychosis) and 155 (Major Depression, Moderate or Severe, without Psychosis)
- –Any conditions previously in V24 HCC 59 that have psychotic features have been moved to HCC 152 with an RAF increase of 0.174-Only one code (C88.0, Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia) was moved to V28 HCC 21 and received a RAF increase of 0.379
- –Any codes relating to manic episodes or bipolar disorder (without psychotic features) have been moved to HCC 154 with an RAF increase of 0.017
- –Most codes relating to major depressive disorder, suicide attempts, and intentional self-harm have been moved to HCC 155 MDD with an RAF decrease of 0.005
- –Important expectations are that V28 has removed codes relating to mild major depressive disorder, depression, or bipolar in remission and any sequela codes relating to self-harm or suicide
V24 HCC 60 has had all its codes transferred to V28 HCC 153 (Personality Disorders; Anorexia/Bulimia Nervosa) with an average RAF increase of 0.154
DoctusTech is helping Value-Based Care organizations evaluate their RAF score in the new v28 model. Do you want to know what your organization's RAF score will look like in the new v28 model? Contact us for a detailed impact assessment analytic report.
12) Spinal Disease Group
Overall the codes in this grouping are largely unchanged. In detail:
V24 HCC 70 (Quadriplegia) has had all of its codes transferred to V28 HCC 180 (Quadriplegia) with a RAF increase of 0.095
V24 HCC 71 (Paraplegia) has had all of its codes transferred to V28 HCC 181 (Paraplegia) with a RAF decrease of 0.100
V24 HCC 72 (Spinal Cord Disorders/Injuries) mostly has had its codes moved to V28 HCC 182 (Spinal Cord Disorders/Injuries) with a RAF decrease of 0.056. Exceptions to this include:
- –Friedrich, cerebellar, and hereditary ataxias have been moved to V28 HCC 200 (Friedreich and Other Hereditary Ataxias; Huntington Disease) with a RAF decrease of 0.199
- –Codes used for sequela to spinal cord injuries have been removed from the model
13) Neurological Disease Group
The changes in this group were mostly to allow for more specific HCCs. Myasthenia gravis now has different HCCs with and without an acute exacerbation. Cerebral palsy is separated based on the presence or absence of quadriplegia, and a new HCC for hereditary movement disorders such as Friedrich’s ataxia was added. In detail:
V24 HCC 73 (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Other Motor Neuron Disease) has had all codes transferred to V28 HCC 190 (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Other Motor Neuron Disease, Spinal Muscular Atrophy) with a RAF increase of 0.637
V24 HCC 74 (Cerebral Palsy) has been split with the single code relating to spastic quadriplegic cerebral palsy moving to V28 HCC 191 (Quadriplegic Cerebral Palsy) with a RAF increase of 0.383, and all other codes moving to V28 HCC 192 (Cerebral Palsy, Except Quadriplegic) with a decrease in RAF by 0.017
V24 HCC 75 (Myasthenia Gravis/Myoneural Disorders and Guillain-Barre Syndrome/Inflammatory and Toxic Neuropathy) has had several significant changes
- -Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuritis and multifocal motor neuropathy have been moved to V28 HCC 193 (Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuritis and Multifocal Motor Neuropathy) with a RAF increase of 0.775
- -The single ICD-10 for myasthenia gravis with acute exacerbation has been moved to V28 HCC 195 (Myasthenia Gravis with (Acute) Exacerbation) with a RAF increase of 2.354
- -Codes relating to Lambert-Eaton, unspecified myoneural disorders, and Myasthenia Gravis without exacerbation have been moved to V28 HCC 196 (Myasthenia Gravis without (Acute) Exacerbation and Other Myoneural Disorders) with a RAF increase of 0.080
- -Many other codes that originally were in V24 HCC 75 were removed from the model, important callouts include the removal of most forms of secondary polyneuropathy (neuropathy due to radiation, drugs, EtOH, inflammatory polyneuropathy, and rheumatoid polyneuropathy
V24 HCC 76 (Muscular Dystrophy) has had all codes transferred to V28 HCC 197 (Muscular Dystrophy) with a RAF decrease of 0.085
V24 HCC 77 (Multiple Sclerosis) has had all codes transferred to V28 HCC 198 (Multiple Sclerosis) with a RAF increase of 0.262
V24 HCC 78 (Parkinson’s and Huntington’s Diseases) mostly had all codes transferred to V28 HCC 199 (Parkinson’s and Other Degenerative Diseases of Basal Ganglia) with a RAF decrease of 0.003 Exceptions to this include:
- -Huntington’s disease has been moved to V28 HCC 200 (Friedreich and Other Hereditary Ataxias; Huntington Disease) with a RAF decrease of 0.284
- -Codes related to secondary or drug-induced parkinsonism have been removed from the model
V24 HCC 79 (Seizure Disorders and Convulsions) has had all codes transferred to V28 HCC 201 (Seizure Disorders and Convulsions) with a RAF increase of 0.012
V24 HCC 80 (Coma, Brain Compression/Anoxic Damage) mostly had all its codes transferred to V28 HCC 202 (Coma, Brain Compression/Anoxic Damage) with a RAF increase of 0.067.
- –The notable exception to this is the removal of codes relating to ‘coma scale, best motor response’ from the model
14) Arrest Disease Group
For the most part codes in this grouping were largely unchanged. In detail:
V24 HCC 82 (Respirator Dependence/Tracheostomy Status) has had all codes transferred to V28 HCC 211 (Respiratory Dependence/Tracheostomy Status/Complications) with a RAF decrease of 0.044
V24 HCC 83 (Respiratory Arrest) has had all codes transferred to V28 HCC 212 (Respiratory Arrest) with a RAF decrease of 0.050
V24 HCC 84 (Cardio-Respiratory Failure and Shock) mostly had all codes transferred to V28 HCC 213 (Cardio-Respiratory Failure and Shock) with a RAF increase of 0.104
- -The notable exception is the removal of codes relating to respiratory conditions that occur after surgery from the model
